Objects Browser
Overview
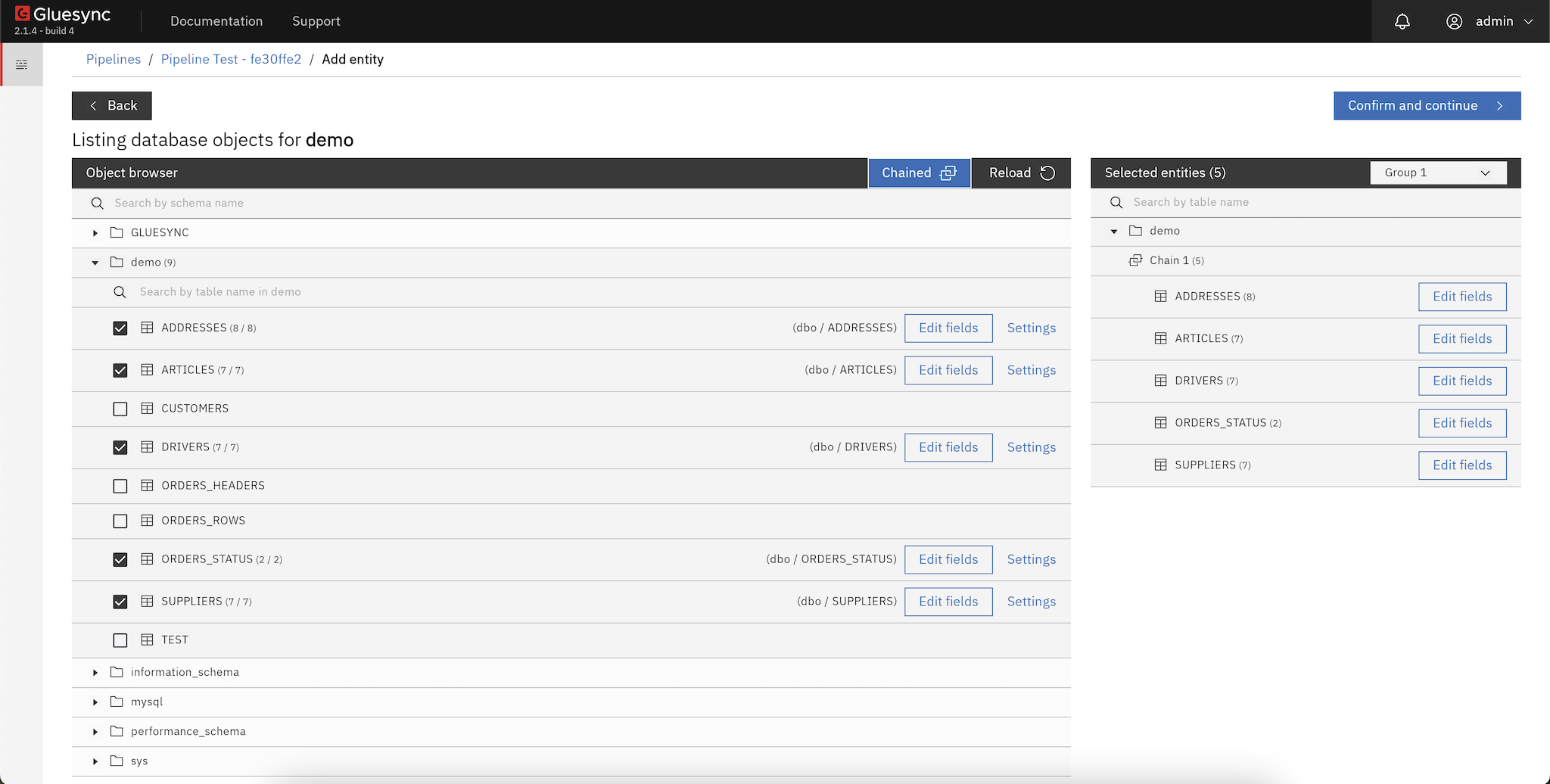
The Objects Browser is the main entry point for creating and editing entities (also called replication tasks) in Gluesync’s Control Plane. It lets you browse the source database objects—such as schemas and tables—search across large datasets, select what to replicate, and associate those selections with a target counterpart.
After you select your desired matches, the Objects Browser provides controls to apply custom settings, edit schema options for source and target fields, create UDFs, define chains, associate entities to groups, and work in bulk.
Key capabilities
-
Browse source-side objects (schemas, tables) and inspect structure.
-
Search and filter to quickly find objects in large datasets.
-
Select one or more tables to replicate.
-
Associate selected source tables with target counterparts.
-
Apply per-entity settings and edit schema mappings for source and target.
-
Create and attach UDFs for custom transformations (learn more).
-
Create chains and associate entities to groups for orchestration (learn more).
-
Perform bulk actions across multiple selected entities.
UI tour
-
Source navigation panel: browse schemas and tables.
-
Main results panel: search results, table lists, and selection checkboxes.
-
Details/config panel: settings, schema editing, target mapping, UDFs, chains/groups.
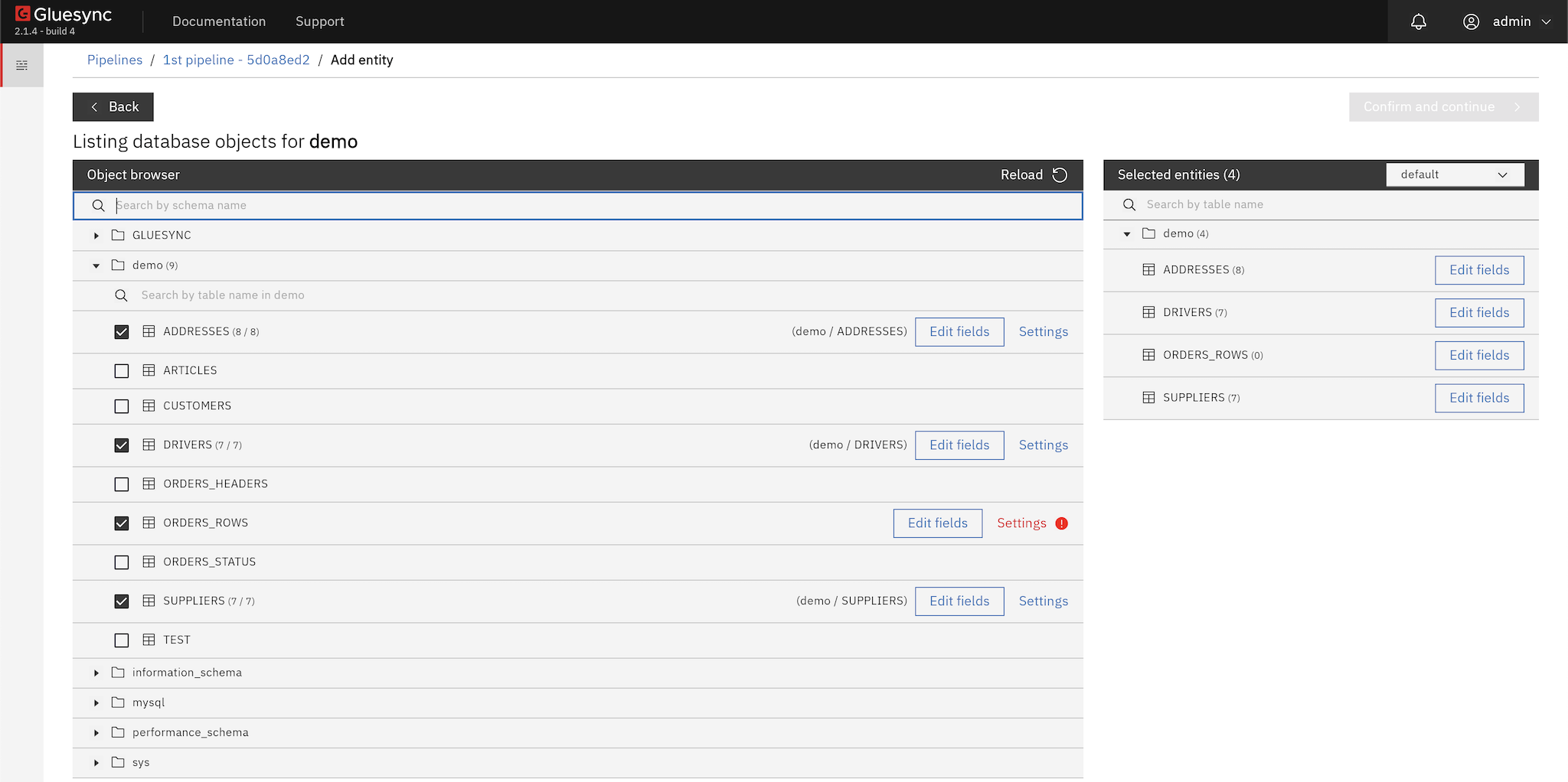
Usage steps
-
Open the Objects Browser from the Control Plane.
-
Use the source navigation and/or search to locate your tables.
-
Select one or more tables you want to replicate.
-
Associate each selection with a target counterpart (existing or new, depending on your target setup).
-
Configure settings and schema options for the selected entity/entities.
-
(Optional) Unlock and customize the target schema if you need additional fields or type changes (Unlock Schema).
-
(Optional) Create or attach a UDF to handle transformations that align source data to your target schema (User Defined Functions).
-
(Optional) Add the entity to a chain or a group to orchestrate execution order and logical grouping (Groups & Chains).
-
Save and deploy your changes.
Working with large datasets
-
Use the search bar to filter by schema, table name, or partial matches.
-
Select multiple tables and apply bulk actions to save time.
Bulk operations
-
Bulk select/deselect tables in the results panel.
-
Apply shared settings (e.g., target mapping defaults) across the current selection.
-
Execute batch schema edits when consistent changes are required across several entities.
|
When applying bulk operations, review exceptions. Some tables may require custom handling due to differing schemas or constraints. |
Advanced actions
-
UDFs: Attach a function to perform validations, transformations, merges, and type conversions during replication. See User Defined Functions.
-
Chains & Groups: Define execution order and logical groupings to coordinate multiple entities. See Groups & Chains.
-
Unlock Schema: When you need to deviate from a 1:1 mapping, customize target columns and data types. See Unlock Schema.
Best practices
-
Start with a small selection to validate mappings and transformations, then scale out.
-
Keep UDFs focused and efficient to maintain throughput.
-
Name technical fields clearly when customizing schemas (e.g.,
source_table,ingestion_ts). -
Test changes in a staging environment before production rollout.
-
Document your mapping and transformation decisions for team knowledge sharing.
Troubleshooting
-
Tables not found: Confirm source connectivity and that the correct schema filters are applied.
-
Target mapping errors: Verify target DDL and permissions, and ensure your mappings align with target constraints.
-
Transformation/type errors: Check UDF logs and confirm that produced values match target column types (see UDFs).
-
Bulk apply differences: Some tables may require overrides; apply per-entity adjustments as needed.